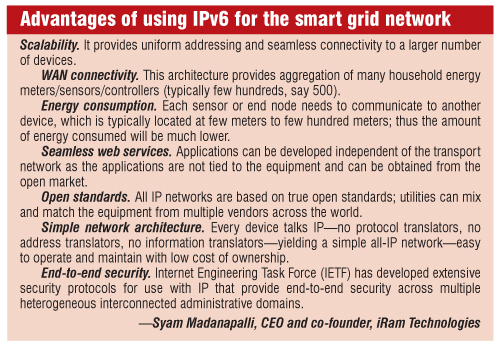
According to him, “Various devices at a given location in the proposed architecture form a mesh using IPv6 and IEEE 802.15.4 and communicate to rest of the smart grid using a border router. These meshes would be replicated throughout the electrical grid and finally connected to utility using appropriate wide area network (WAN) technologies that are commercially available from the telecom operators or ISPs.”
Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) and distribution automation. AMI is being more deeply integrated into the grid, and its projects are increasingly implemented by utilities, particularly for use in distribution automation (DA) applications.
AMI networks require robust communications between individual meters and data concentrators. They use either RF mesh or RF star topology, or implement PLC.
For example, to implement AMI, an IPv6-based wireless communication module is attached/integrated into the home energy meter. Few hundreds of homes in a given locality can form a mesh and connect to the utility using one-gateway routers. An additional border router can be provided for load balancing and redundancy purpose.
Automated test equipment. The current slew of smart-grid test equipment is automated systems that can test all kinds of relays from manufacturers including ABB and Siemens, as well as different kinds of protection such as overcurrent, distance, differential and generator protection. When enquired about an instrument named smart Megger relay tester (SMRT), a senior engineer explained that conventional test equipment was fully manual and, as with any manual labour, there is a certain amount of human error that is introduced. Modern automated equipment takes away human error and also reduces the amount of work that he/she has to put in.
The voltage levels faced whilst testing circuit breakers are very dangerous. “Modern equipment allows you to do dual-ground testing, which enhances safety levels considerably. Conventionally, with both sides grounded, you are unable to even make a measurement, but our new solution is so unique in that this can be carried out,” explains Ajay Goyal, managing director, Megger (India).
A switchgear will have electrical disconnect switches, fuses or circuit breakers used to control, protect and isolate electrical equipment. V. Narayanan, senior application engineer, Megger (India), says, “To check one switchgear, they needed the help of two to three people in order to test it properly. A new tool targeting this problem is the protection condition analyser. This tool allows to test simultaneously all of the key elements of substation protection systems—including protection relay, circuit breaker, DC system and protection circuitry—even whilst the system is on-load. Once the test is completed, it outputs the results on the display.
Multiphysics simulation. The huge engineering project of migrating the electrical grid to a smart grid involves modernising several electrical components. For engineers at ABB Corporate Research Power Technologies in Sweden, multiphysics tools have proved an invaluable tool for modelling the coupled electromagnetic, thermal and fluid phenomena that take place within these systems.
Data modelling and forecasting
This is where all the data gathered by the sensors, smart meters and other equipment are put into use.
Avoid gold plating the electrical grid. Unlike how it sounds, ‘gold plating’ is where everything is over-designed to be safe, by going overboard with thresholds and limitations. Without smart technology to optimise the operation of the power network, gold-plating has been a common approach to ensure that the network is not going to melt during abnormal events.
One of the approaches to overcome gold-plating is the dynamic rating of equipment. This can be applied to overhead lines, underground cables, transformers, etc.
“A recently developed, groundbreaking technology is a 3D model of the electricity network which provides numerous applications including modelling and forecasting applications. An aeroplane loaded with sensors is flown over the network, where it gathers Lidar data point and other relevant data—such as temperature, wind speed, electromagnetic field, heatmaps, etc. An algorithm is run over the Lidar data to automatically extract the utility’s assets, resulting into a 3D model and exact position of the utility’s assets and nearby environment such as trees,” explains Diethelm.
Is an automated power grid secure?
In addition to terrorist activities, natural disasters and ageing equipment can also bring down the electrical grid. Cumulative smart-grid cyber security investment from 2011 to 2018 will total $14 billion, forecasts Pike Research.
“This requires a better emergency management system with appropriate electronic access control and video surveillance to mitigate problems. The system should also be able to isolate problems and restore electrical services as quickly as possible when disaster happens,” says Madanapalli. The existing SCADA systems are more prone to cyber attacks as the utilities start using more and more computer-based applications without an end-to-end design for the smart grid implementation.
The author is a senior technical correspondent at EFY, Bengaluru